Africa – A Continent of Rich History and Diverse Geography
Africa is a land of ancient civilizations, diverse cultures, and breathtaking landscapes. From the Sahara to the Nile, its history is deep and geography vast—home to deserts, rainforests, mountains, and the cradle of human evolution.
Africa – A Continent of Rich History and Diverse Geography
Africa is more than just a landmass—it's the birthplace of humanity, a continent of kingdoms and empires, deserts and rainforests, vibrant cultures, and resilient people. From the golden sands of the Sahara to the lush rainforests of the Congo, and from the peaks of Kilimanjaro to the ancient temples along the Nile, Africa's story is vast, complex, and beautiful.
🌍 Geography: The Shape of a Continent
Covering over 30 million square kilometers, Africa is the second-largest continent in both area and population. It is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Red Sea to the northeast. Africa is home to 54 recognized countries, 2 disputed territories, and over 1.4 billion people.
Despite being portrayed as a flat continent in some outdated maps, Africa is a land of incredible physical diversity:
-
🏜️ The Sahara Desert dominates the north, stretching across 11 countries and covering more area than the United States.
-
🌄 Mount Kilimanjaro, in Tanzania, rises to 5,895 meters—Africa’s highest point and a world-renowned trekking destination.
-
🌊 The Nile River, flowing north for about 6,650 kilometers, is one of the longest rivers in the world, vital to civilizations for millennia.
-
🌳 The Congo Basin, with the second-largest rainforest after the Amazon, teems with biodiversity.
-
🌿 The Great Rift Valley slices through East Africa, creating dramatic landscapes, active volcanoes, and deep lakes like Lake Tanganyika and Lake Malawi.
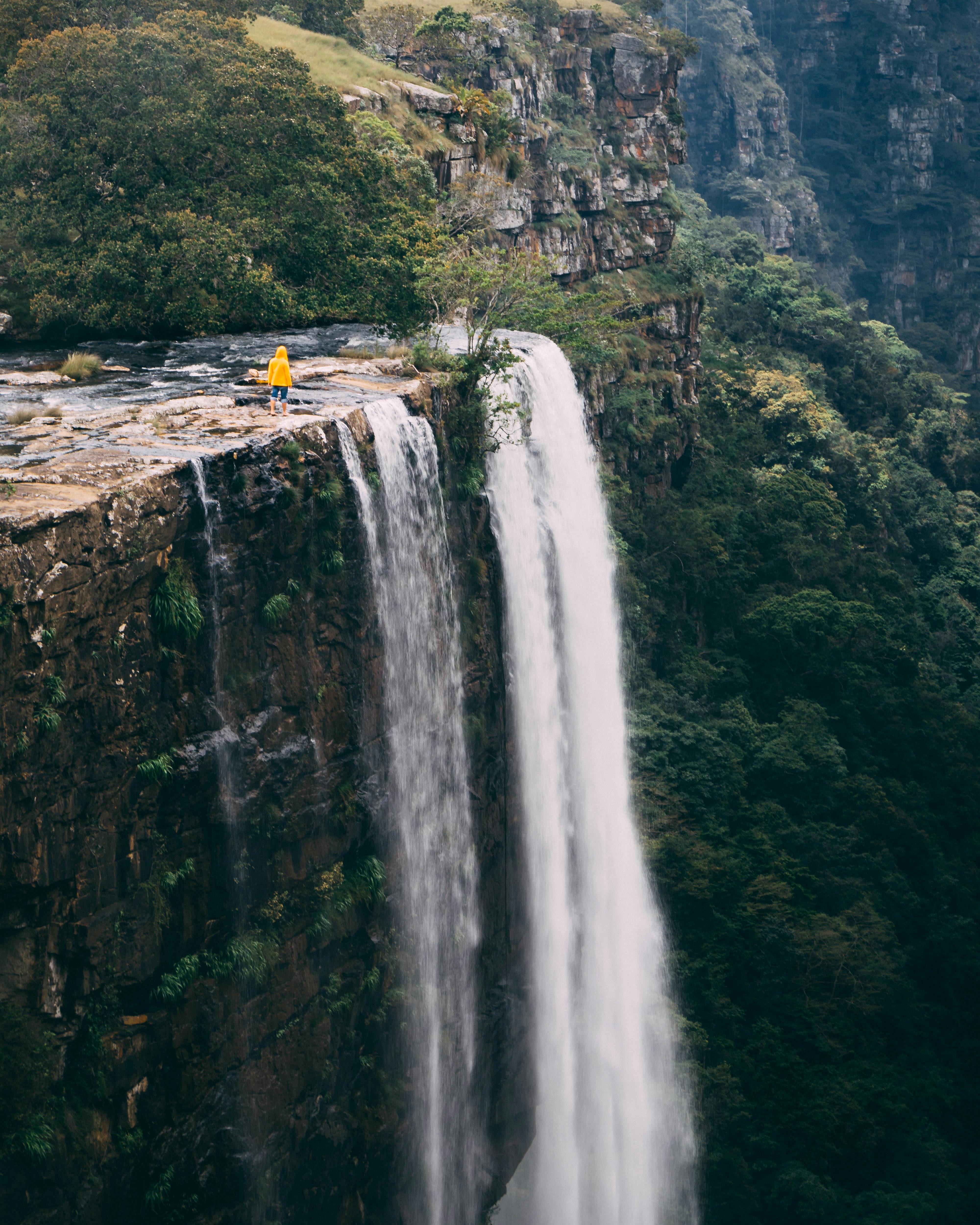
Africa’s climate zones vary from tropical rainforests to arid deserts to Mediterranean coasts and alpine highlands. This variation contributes to its status as one of the most ecologically diverse regions on Earth.
📖 History: The Cradle of Humankind
Africa is not just geographically ancient—it’s historically foundational. Fossils of early humans such as Australopithecus afarensis and Homo habilis were discovered in East Africa, earning it the title: “Cradle of Humanity.”
🏛️ Ancient African Civilizations
Long before European exploration, Africa had thriving civilizations:
-
Ancient Egypt: Along the fertile Nile Valley, the Egyptians developed writing (hieroglyphics), monumental architecture (pyramids, temples), medicine, and advanced agriculture. They traded with neighboring civilizations and left behind a written legacy studied worldwide.
-
Nubia and the Kingdom of Kush: Located south of Egypt, these powerful civilizations sometimes ruled Egypt itself. They built pyramids, traded gold and ivory, and developed their own script.
-
Carthage (Modern Tunisia): A maritime power founded by Phoenicians, Carthage was Rome’s great rival in the Punic Wars before its destruction in 146 BCE.
-
Kingdom of Axum (Ethiopia): One of the oldest Christian kingdoms in the world, known for its obelisks, coinage, and control of Red Sea trade routes.
-
Mali Empire (West Africa): A rich and powerful empire that flourished in the 13th–16th centuries. Its most famous ruler, Mansa Musa, is often cited as the wealthiest individual in history. His pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 is legendary for the gold he distributed along the way.
-
Great Zimbabwe: A stone-walled city in southern Africa, it served as a center of trade, wealth, and culture from the 11th to 15th centuries.
These civilizations contributed to global knowledge in architecture, astronomy, mathematics, governance, and trade.
🛡️ Colonialism: The Disruption of a Continent
In the late 19th century, European powers carved up Africa during the Berlin Conference of 1884–85, often ignoring existing kingdoms, ethnic divisions, and cultures. Countries like Britain, France, Germany, Portugal, Belgium, and Italy colonized nearly the entire continent.
Colonialism imposed foreign governance, extracted natural resources, disrupted economies, and created artificial borders—laying the foundation for many modern conflicts.
🕊️ Decolonization and Modern Africa
After World War II, a wave of independence movements swept across the continent. Ghana became the first sub-Saharan African country to gain independence in 1957. Throughout the 1950s–70s, dozens of nations followed.
Leaders like:
-
Kwame Nkrumah (Ghana)
-
Julius Nyerere (Tanzania)
-
Nelson Mandela (South Africa)
-
Patrice Lumumba (Congo)
...led movements for liberation, pan-African unity, and development.
🧬 Cultural Diversity and Language
Africa is home to over 1,500 languages spoken across thousands of ethnic groups. Major language families include:
-
Afroasiatic (Arabic, Amharic, Somali)
-
Niger-Congo (Yoruba, Swahili, Zulu, Igbo)
-
Nilo-Saharan
-
Khoisan (famous for click consonants)
Cultural expressions range from the tribal masks of West Africa to the beadwork of the Maasai, from Nubian architecture to Malian music, and from Moroccan cuisine to Ethiopian coffee rituals.
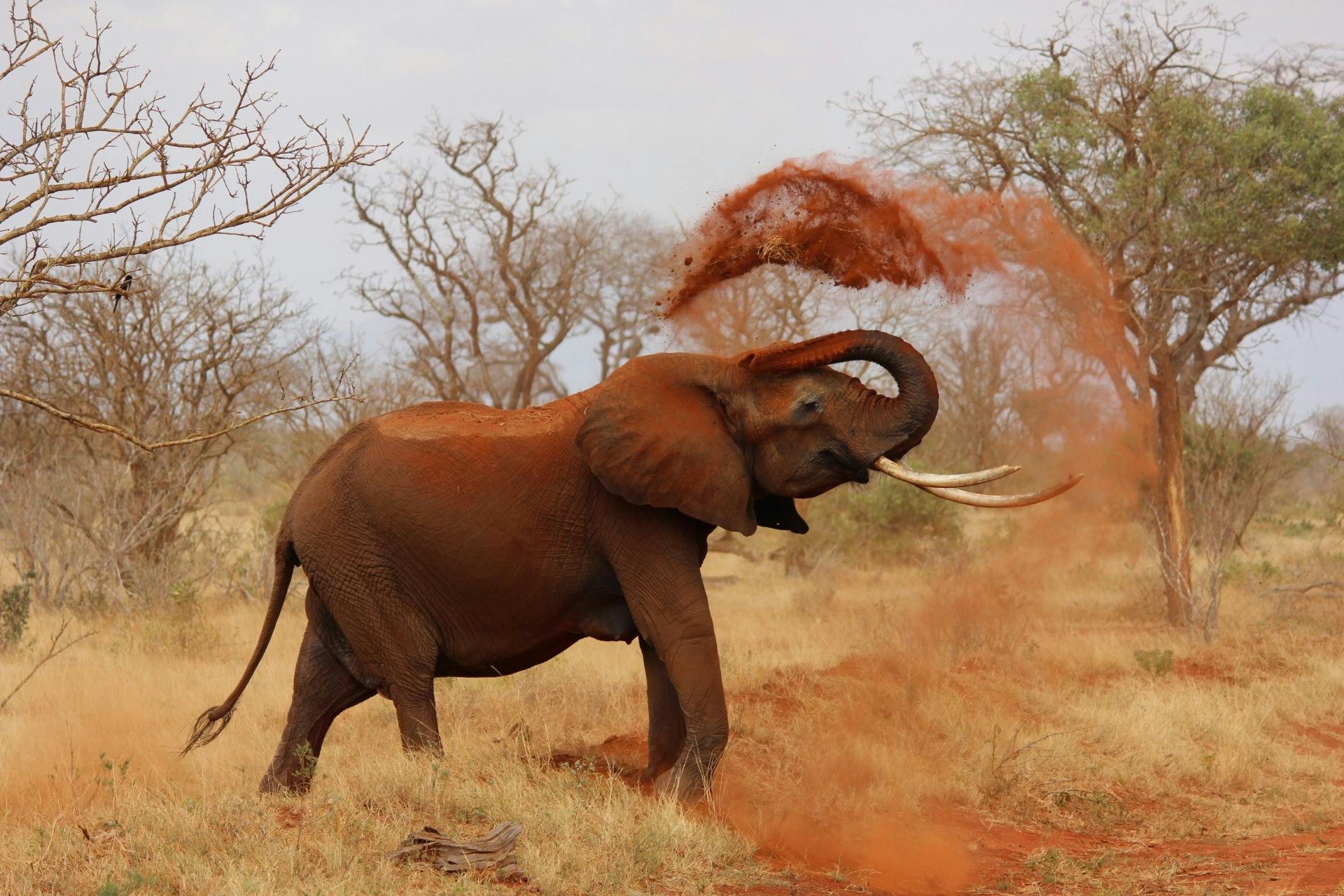
🐘 Natural Resources and Wildlife
Africa is incredibly rich in natural resources, including:
-
Minerals: Gold, diamonds, cobalt, uranium, copper
-
Oil & Gas: Nigeria, Angola, Algeria, Libya
-
Agriculture: Cocoa (Ivory Coast, Ghana), Coffee (Ethiopia, Kenya), Tea (Rwanda)
The continent is also a wildlife haven. The Big Five—lion, elephant, leopard, rhinoceros, and buffalo—roam parks and reserves like:
-
Serengeti National Park (Tanzania)
-
Kruger National Park (South Africa)
-
Maasai Mara (Kenya)
-
Okavango Delta (Botswana)
Africa’s biodiversity includes rare species like the okapi, shoebill stork, African wild dog, and gorillas of the Congo Basin.
🏙️ Modern Africa: A Rising Continent
Despite its challenges, modern Africa is dynamic and forward-looking:
-
Technology hubs in Kenya (Silicon Savannah), Nigeria (Lagos), and South Africa are reshaping business.
-
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is the world’s largest free trade area by country count.
-
A young population (median age ~19 years) is fueling innovation, education, and culture.
-
Cities like Nairobi, Cape Town, Addis Ababa, Dakar, and Accra are becoming global centers for arts, fintech, design, and tourism.
🚧 Challenges and Hope
Africa faces issues like poverty, unemployment, political instability, conflict, and climate change. Yet across the continent, people are:
-
Building solar-powered villages
-
Launching tech startups
-
Advocating for women’s rights
-
Reclaiming cultural heritage
-
Promoting African identity through music, cinema, and fashion
🌍 Why Africa Matters
Africa isn’t one story—it’s many stories, stretching from ancient rock paintings in Namibia to futuristic skyscrapers in Rwanda.
-
It’s where humans first walked upright.
-
It’s where empires rose and fell, leaving ruins and wisdom behind.
-
It’s where drums beat, dances swirl, and languages echo in countless dialects.
-
It’s a continent that endures, grows, and aspires.
Africa is not a mystery to be solved—it is a world to be understood.
“To ignore Africa is to ignore the roots of the world itself.”






Comments (0)
Please login to leave a comment.